How to remotely debug workers
Remote debugging allows you to introspect and even manipulate the state of a worker and can be applied to either Code Studios or Persistent Queries. You may want to debug a worker to examine the state of a Deephaven object, or to examine and step through your own Java extensions.
To debug a Deephaven worker, you should create an IntelliJ project that includes the Deephaven JARs and any of your own components.
- When debugging a Legacy worker, you must create a project with the Legacy JARs.
- When debugging a Core+ worker, you must create a project with Deephaven Core+ and Deephaven Community Core JARs.
There are two modes of remote debugging available:
- Attaching to a remote JVM. In this mode, you start the worker first and then start the debugger second.
- Listening to a remote JVM. In this mode, you start the debugger first and then start the worker second.
In either case, you must add additional options to your worker's JVM arguments. From the Code Studio, set the arguments in the Extra JVM Arguments text box after expanding Show Advanced:
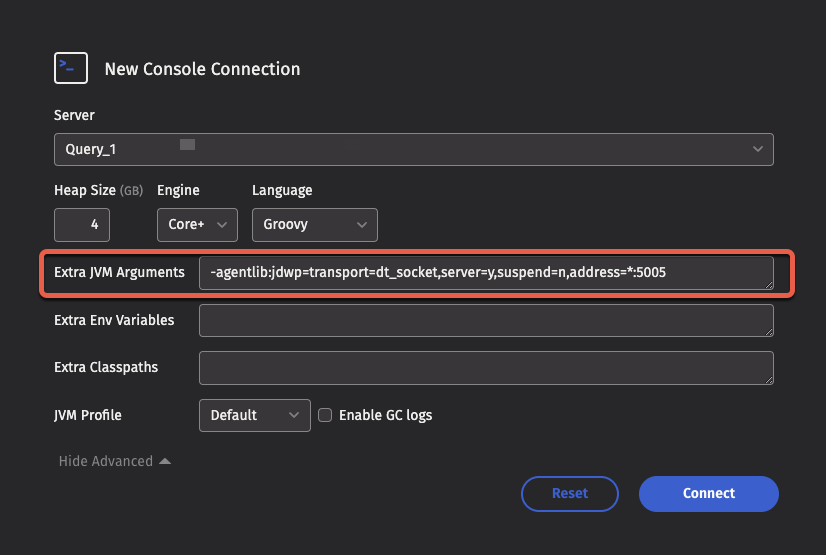
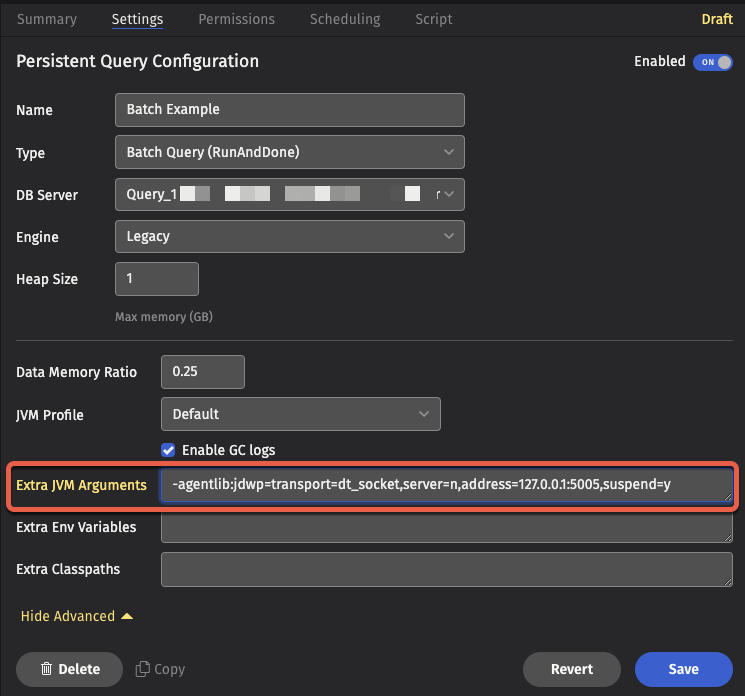
For a Persistent Query, set Extra JVM Arguments after expanding Show Advanced in the Settings tab:
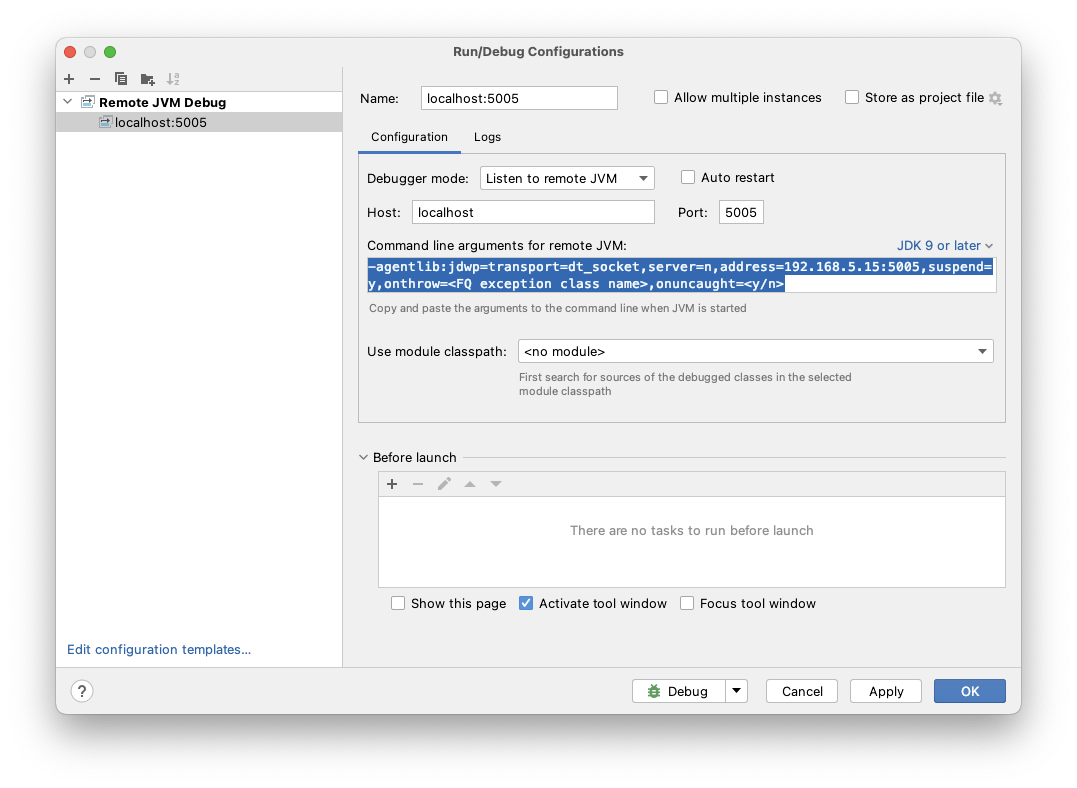
IntelliJ run configuration
The Jetbrains remote debugging tutorial describes how to configure an IntelliJ run configuration attaching or listening to a remote JVM. The configuration for "Remote JVM Debug" allows you to select the debugging mode, the port, and if applicable the remote hostname. Command Line Arguments for remote JVM: in this dialog serve as a suitable template for the extra JVM arguments to provide to your worker:
Attaching to a remote JVM
Typical worker JVM arguments to start a JVM that listens for connections from a remote debugger (i.e., the IntelliJ debugger attaches to a remote JVM):
Note
Each listening JVM must have a unique port, otherwise the worker will fail to start with an error of the form:
Warning
When attaching to a remote JVM, setting suspend=y is necessary to debug worker startup, but prevents the worker startup process from proceeding until you connect your debugger to the worker. If you do not connect a debugger quickly enough, then the worker startup times out and fails. Consider using a listening debugger instead. When debugging script code in a Code Studio, you can select suspend=n and attach the debugger before executing your script code.
Listening to a remote JVM
Typical worker JVM arguments to make it connect to a listening debugger (i.e., the IntelliJ debugger is listening to a remote JVM):
Make sure your listening debugger and any applicable SSH port forwarding is enabled before starting your worker.
SSH Port Forwarding
Remote debugging requires TCP connectivity between your local IDE and the worker on your selected port. Depending on your network, VPN, and firewall configuration it may be necessary or easier to use SSH tunnels to establish the necessary connectivity.
For example, if you have a worker that is listening on port 5050 on the host worker-host.example.com and you want to connect to port 5005 from IntelliJ, you could execute the following SSH command to create a tunnel that forwards port 5005 on your local machine to port 5050 on the remote machine:
The -N option instructs SSH not to open an interactive shell, instead only the tunnel is opened. Adding the -v option can sometimes be useful to troubleshoot connectivity issues.
If your debugger is listening on port 5006, and you've configured a worker on worker-host.example.com to connect to 5060 on startup, the following SSH command to create the tunnel: