Component Rules
This guide presents some important rules to remember for deephaven.ui components when writing queries.
Children and props
Arguments passed to a component may be either children or props. Children are positional arguments passed to a parent component. Props are keyword arguments that determine the behavior and rendering style of the component. The child positional arguments must be passed first in the desired order. The prop keyword arguments can then be added in any order. Placing a prop before a child argument will cause the child to be out of order.
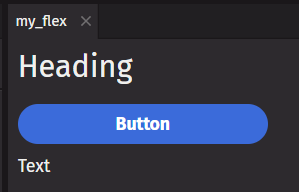
In the above example, the flex component is the parent. It has three children: a heading, a button, and a text component. These children will be rendered inside the flex. It also has three props: direction, wrap, and width. These three props indicate that the flex should be rendered as a 200 pixel column with wrap enabled.
Comparison with JSX
For developers familiar with React JSX, this example shows how prop and child arguments are specified in JSX.
Here is the same component written in deephaven.ui.
Define your own children and props
To define children and props for a custom component, add them as arguments to the component function. As a convention, you may declare the children using the * symbol to take any number of arguments.
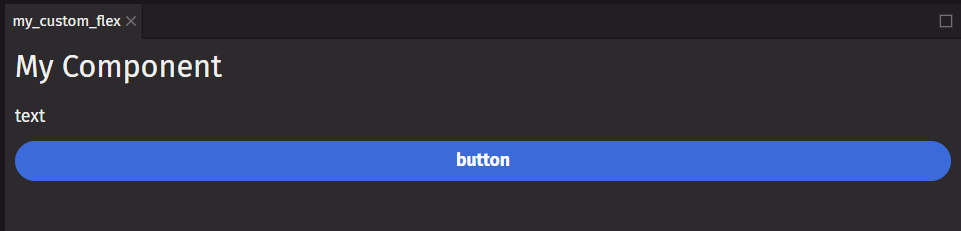
Component return values
A deephaven.ui component usually returns a component. However, it may also return:
- a list or tuple of components.
Noneif it should perform logic but does not need to be rendered.- a single value like a
stringorint.
Conditional return
Return statements can be conditional in order to render different components based on inputs.