How to run full Garbage Collection
This guide shows how to perform full Garbage Collection (GC) using the convenience method garbage_collect.
Garbage collection is a memory management process that automatically collects unused objects created on the heap and deletes them to free up memory. The garbage_collect method performs GC in Python first; then, the underlying JVM runs its garbage collector twice due to the cross-referencing nature of the Python/Java integration in Deephaven.
Note
Since there is no way to force the Java garbage collector to run, the effect of calling this function is non-deterministic. Users should also be mindful of the overhead that running garbage collection generally incurs.
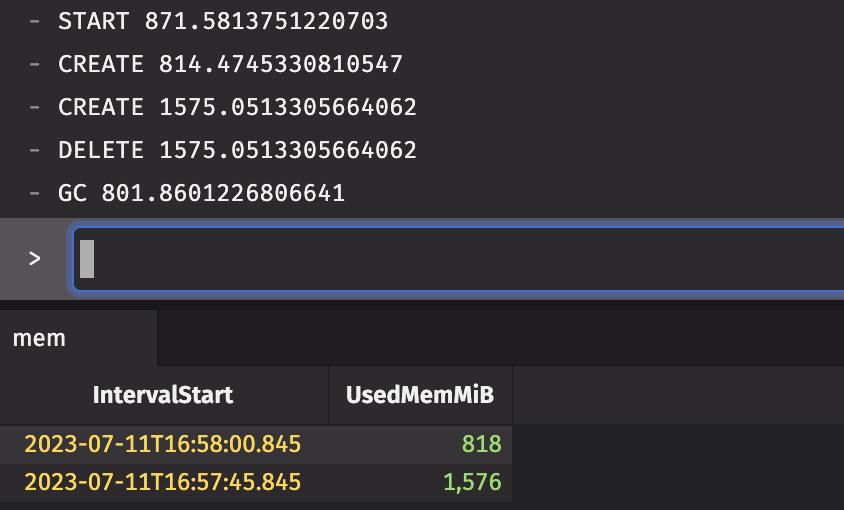
Example
In this example, we use Deephaven's Performance Monitor library's server_state method to print the amount of memory Deephaven is currently using at various points throughout the query. This shows memory consumption at the beginning, when objects are created and deleted, and then after garbage_collect is called. The garbage_collect method does not take any arguments. The data in the UsedMemMiB column tracks how much memory is currently being used.