Create a hierarchical tree table
This guide will show you how to create a hierarchical tree table. A tree table is a table with an expandable tree structure, as seen in the diagram below:
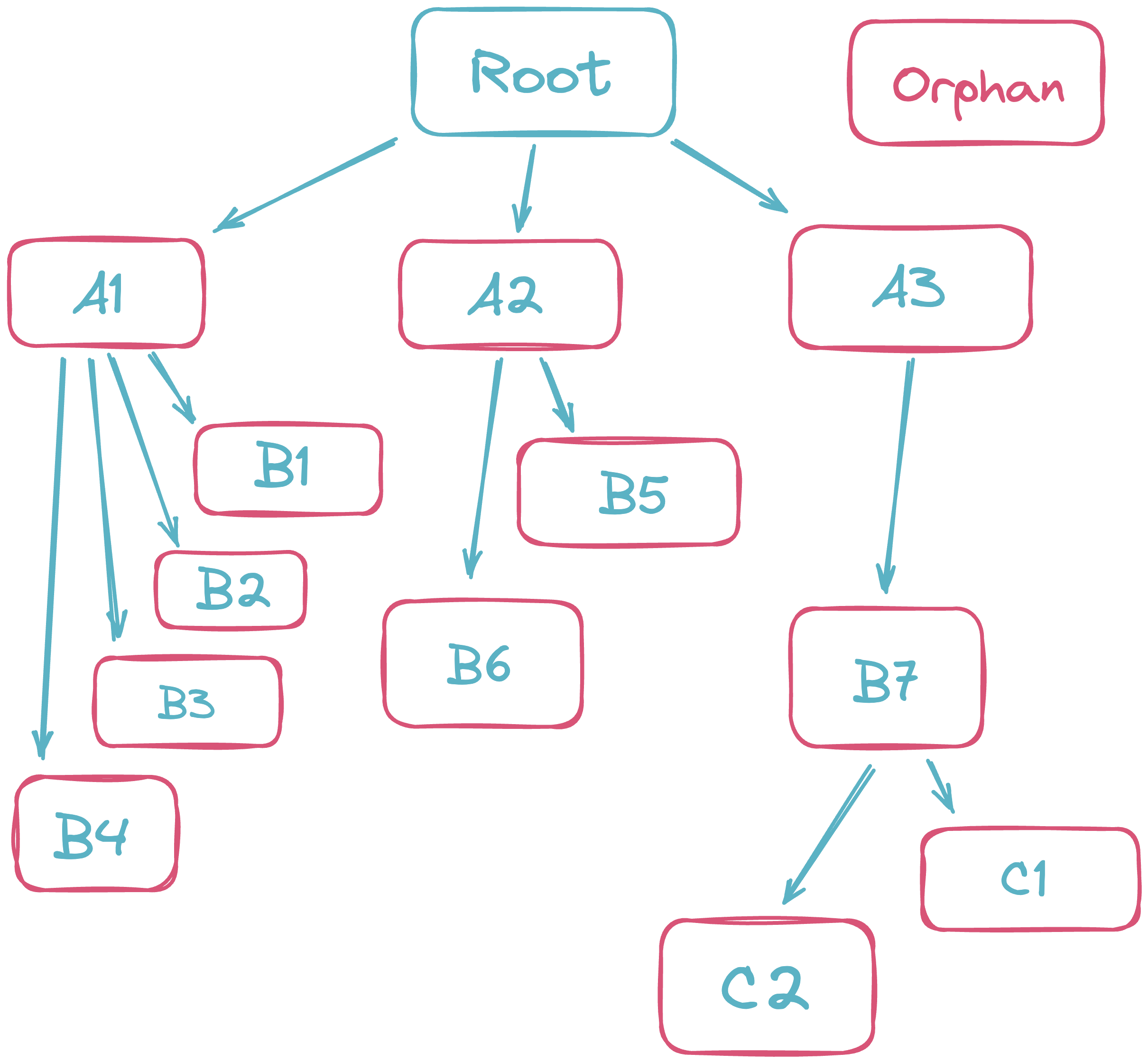
In computer science, trees are data structures used to represent hierarchical relationships between pieces of data. The data within the tree is stored in nodes, which are represented by the boxes in the diagram above.
Every tree table has one (and only one) root node, which is the topmost node in the tree. Aside from the root node, all other nodes in the tree follow the same rules: each node can have one (and only one) parent, and zero or more children. In the diagram above, B7's parent is A3, and its children are C1 and C2. Nodes with no children are known as leaf nodes, or leaves, as they are the terminal nodes of the tree structure. B3 and C1 are both leaves in the diagram above.
A node with no parent is known as an orphan, and will appear in the table outside of the tree structure.
tree
In Deephaven, tree tables are created using the tree method:
result = source.tree(idColumn, parentColumn)
Where:
idColumnis the name of the column that contains the unique identifier for each node in the tree.parentColumnis the name of the column that contains the unique identifier for the parent of each node in the tree.
The resulting table is initially collapsed, only showing the root node. Clicking on that node will expand it to show its children, and so on. Rows in the initial table with a parentCol value equal to a row in the idCol column will appear as children of the parent row.
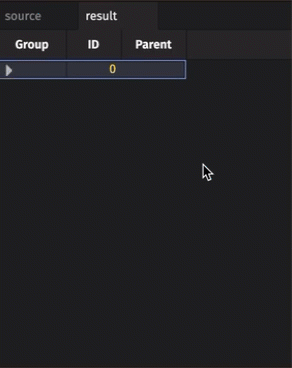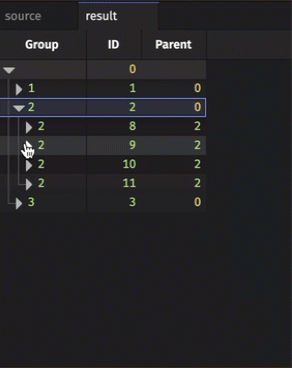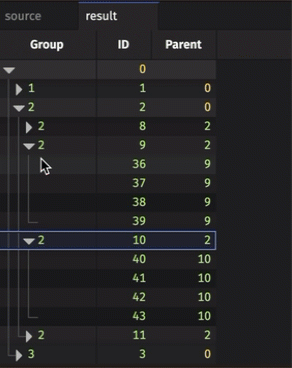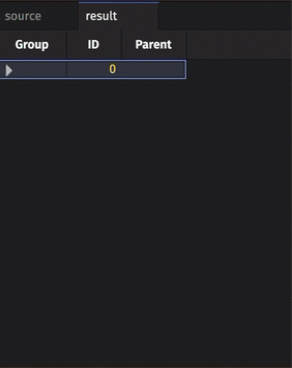
Examples
Static data
The first example creates two constituent tables, which are then joined together to form the source table. The ID and Parent columns in source are used as the ID and parent columns, respectively.
source = emptyTable(100).updateView("ID = i", "Parent = i == 0 ? NULL_INT : (int)(i / 4)")
result = source.tree("ID", "Parent")
Real-time data
Tree tables work in real-time applications the same way as they do in static contexts. This can be shown via an example similar to the one above.
t1 = emptyTable(10_000).updateView("ID = i", "Parent = i == 0 ? NULL_INT : (int)(i / 10)")
t2 = timeTable("PT0.01S").updateView("I = i % 10_000").lastBy("I")
source = t1.join(t2, "ID = I")
result = source.tree("ID", "Parent")
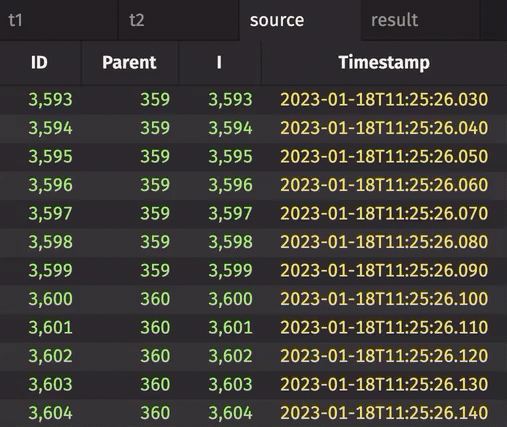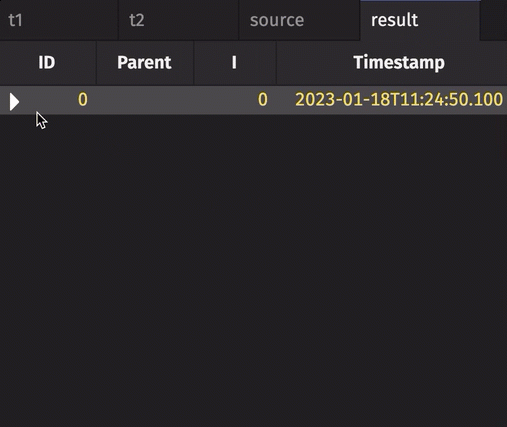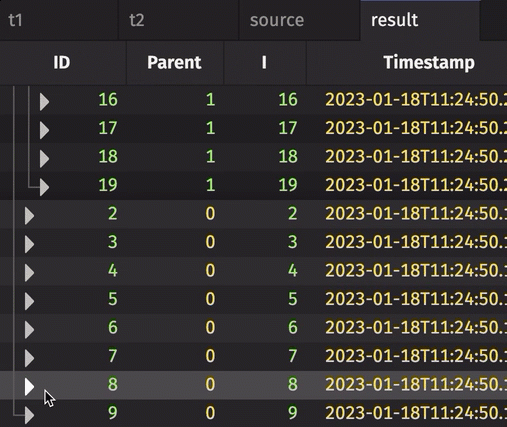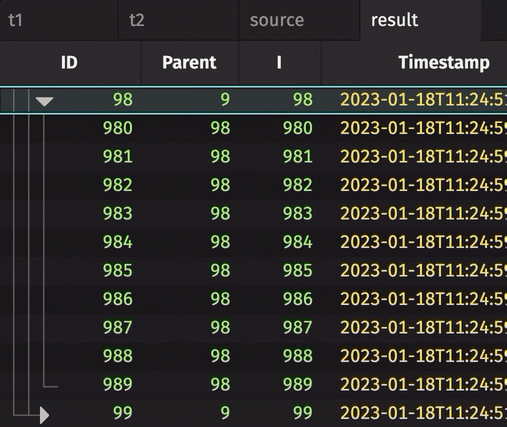
Orphan nodes
Rows (nodes) in a tree table are considered "orphans" if:
- The node in question is not the root node.
- The node's parent is not null.
- The node's parent does not exist in the table.
Non-root nodes where the parent is null are not considered orphans. They can appear in the tree table, but they will always appear outside of the tree structure. For example, see rows 102 and 103 in the following figure:
Note that these rows appear on the same level as the root node, outside of the tree structure.
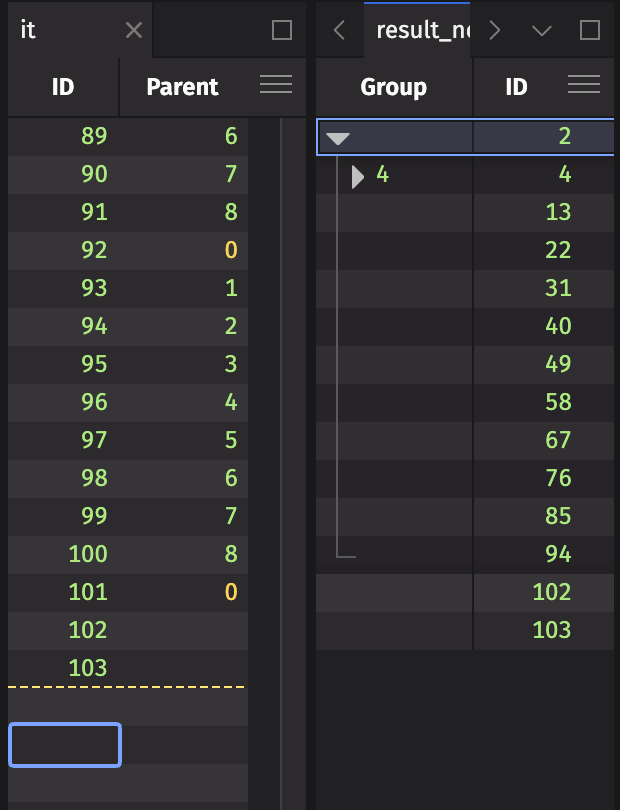
Orphan nodes appear outside of the tree table's tree structure by default. In order to include orphans in a tree table as children of the root node, the TreeTable class's promoteOrphans method can be invoked before creating the tree table with tree.
The following example shows how the resulting tree table changes if orphans are promoted.
import io.deephaven.engine.table.hierarchical.TreeTable
source = emptyTable(100).updateView("ID = i + 2", "Parent = i == 0 ? NULL_INT : i % 9")
resultNoOrphans = source.tree("ID", "Parent")
resultWithOrphans = TreeTable.promoteOrphans(source, "ID", "Parent").tree("ID", "Parent")