Create and use input tables
Input tables allow users to enter new data into tables in two ways: programmatically, and manually through the UI.
In the first case, data is added to a table with add, an input table-specific method similar to merge. In the second case, data is added to a table through the UI by clicking on cells and typing in the contents, similar to a spreadsheet program like MS Excel.
Input tables come in two flavors:
- append-only
- An append-only input table puts any entered data at the bottom.
- keyed
- A keyed input table supports modification/deletion of contents, and allows access to rows by key.
We'll show you how to create and use both types in this guide.
Create an input table
First, you need to import the input_table method from the deephaven module:
An input table can be constructed from a pre-existing table or a list of column definitions. In either case, one or more key columns can be specified, which turns the table from an append-only input table to a keyed input table.
From a pre-existing table
Here, we will create an input table from a table that already exists in memory. In this case, we'll create one with empty_table.
From scratch
Here, we will create an input table from a list of column definitions. Column definitions must be defined in a dictionary.
The resulting table is initially empty, and ready to receive data.
Create a keyed input table
In the previous two examples, no key column was specified when creating the input tables. If one or more key columns is specified, the table becomes a keyed table.
Let's first specify one key column.
In the case of multiple key columns, specify them in a list.
When creating a keyed input table from a pre-existing table, the key column(s) must satisfy uniqueness criteria. Each row or combination of rows in the initial table must not have repeating values. Take, for instance, the following table:
A keyed input table can be created from the X and Y columns, since they have no repeating values, and are thus unique:
A keyed input table cannot be created from the Sym or Marker columns, since they have repeating values and combinations, and are thus not unique:
Add data to the table
Programmatically
You can add data to input tables in two ways:
New data is added to the end of the input table. If the input table is keyed, the new data will overwrite any existing data with the same key.
Note
To programmatically add data to an input table, the table schemas (column definitions) must match. These column definitions comprise the names and data types of every column in the table.
Data can also be added to an input table asynchronously. Asynchronous function calls in the same thread are queued and processed in order. However, ordering is not guaranteed across threads. The following code block asynchronously adds data to a keyed input table:
Important
Asynchronous adds can only be done on keyed input tables.
Manually
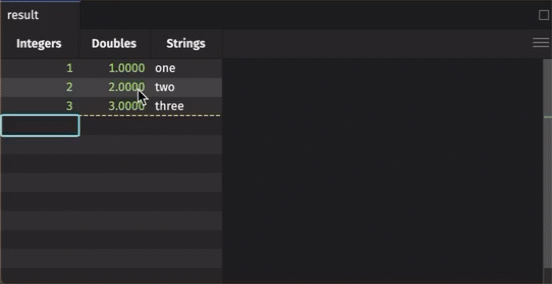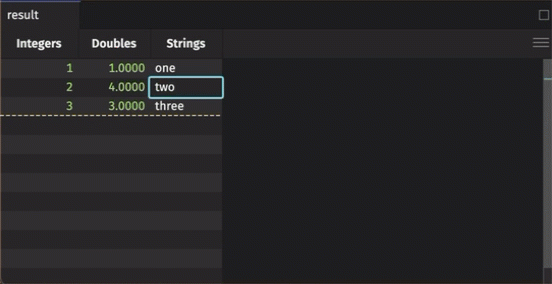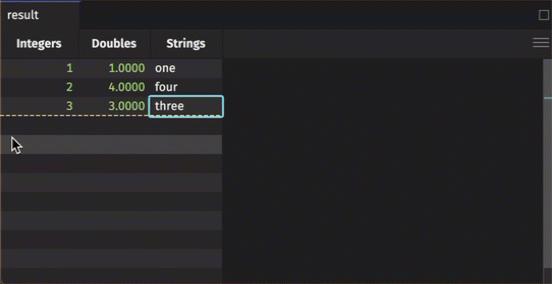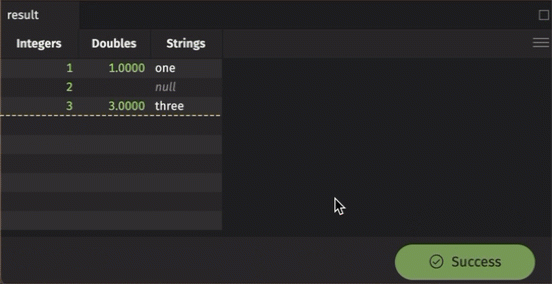
To manually add data to an input table, simply click on the cell in which you wish to enter data. Type the value into the cell, hit enter, and it will appear.
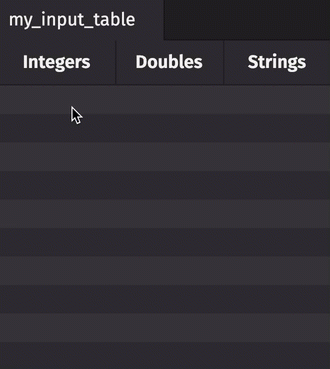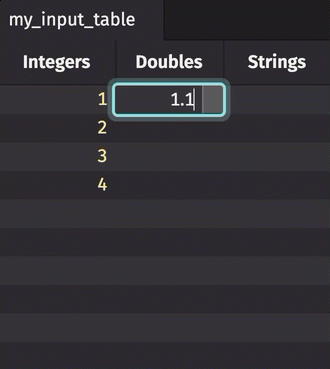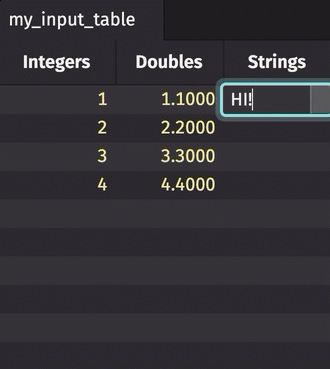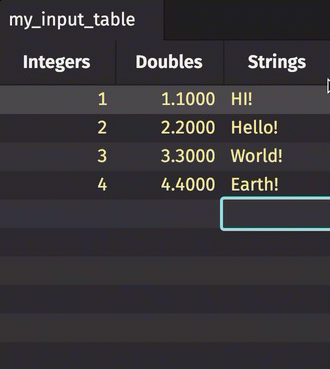
Note that with a keyed input table, you can edit existing rows; however, adding a new row will erase previous rows with the same key.
Important
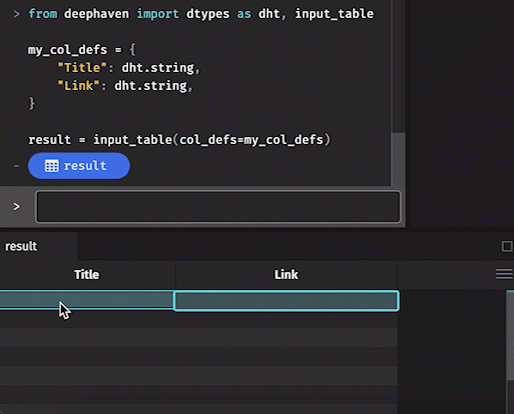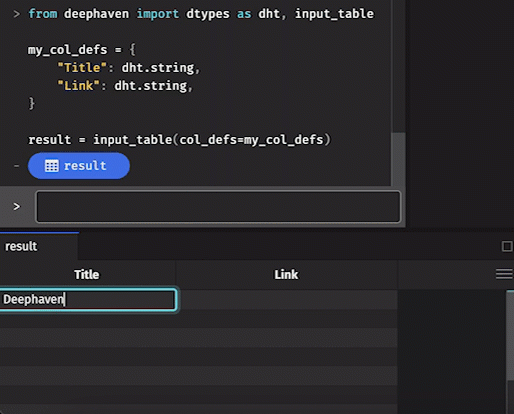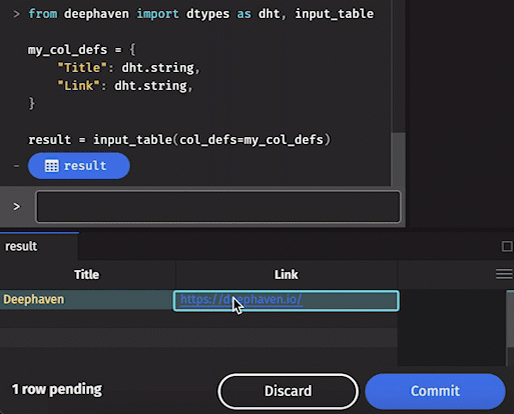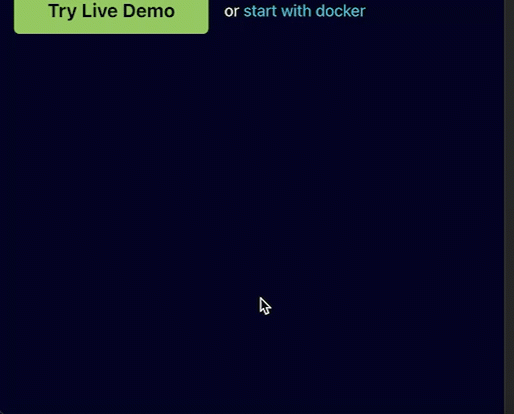
Added rows aren't final until you hit the Commit button. If you edit an existing row in a keyed input table, the result is immediate.

Here are some things to consider when manually entering data into an input table:
- Manually entered data in a table will not be final until the Commit button at the bottom right of the console is clicked.
- Data added manually to a table must be of the correct type for its column. For instance, attempting to add a string value to an int column will fail.
- Entering data in between populated cells and hitting Enter will add the data to the bottom of the column.
Delete data from a table
Data can only be deleted from a keyed input table. To delete data from a keyed input table, use one of the following methods:
delete: Synchronous deletion.delete_async: Asynchronous deletion.
To delete table data, supply only the key values of the rows you wish to delete. For instance, in the previous section, we created a keyed input table where the key column is called Key. The following code deletes a row with the key value A:
The same applies for asynchronously deleting data from a keyed input table. The following code block asynchronously deletes a row with the key value B:
Note
Asynchronous functions calls in the same thread are queued and processed in order. However, ordering is not guaranteed across threads.
Clickable links
Any string column in Deephaven can contain a clickable link — the string just has to be formatted correctly.
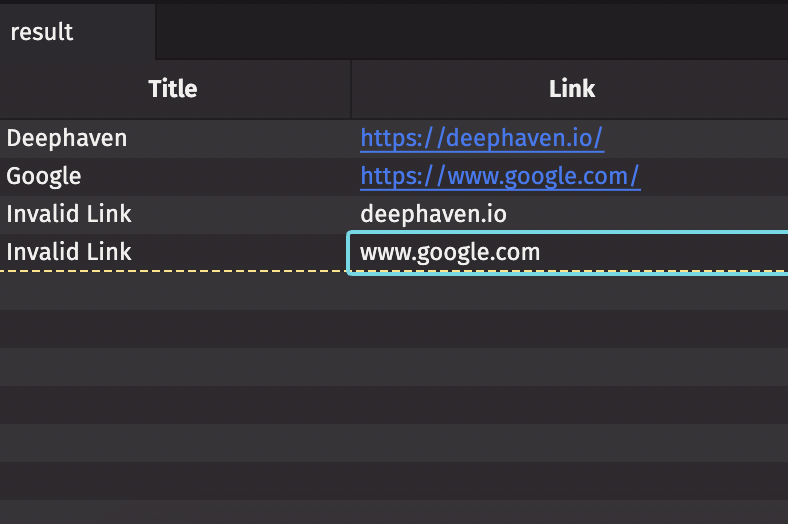
Let's create an input table that we can add links to manually: