tree
The Deephaven tree method creates a tree table from a source table given an ID column name and parent column name.
Syntax
source.tree(id_col: str, parent_col: str, promote_orphans: bool = False) -> TreeTable
Parameters
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| id_col | str | The name of the ID column. |
| parent_col | str | The name of the parent column. |
| promote_orphans optional | bool | Whether to promote node tables whose parents do not exist to be children of the root node. The default is |
Returns
A tree table.
Examples
The following example creates a tree table from a static table.
from deephaven.constants import NULL_INT
from deephaven import empty_table
source = empty_table(100).update_view(
["ID = i", "Parent = i == 0 ? NULL_INT : (int)(i / 4)"]
)
result = source.tree(id_col="ID", parent_col="Parent")
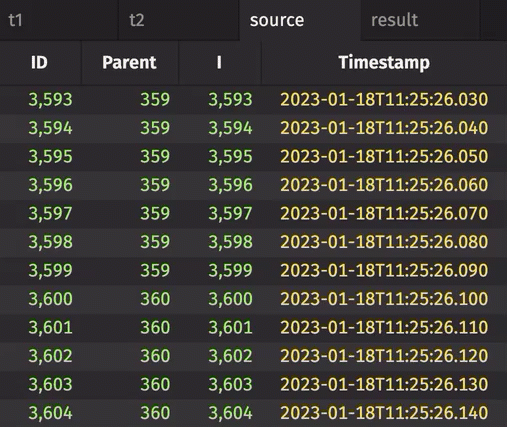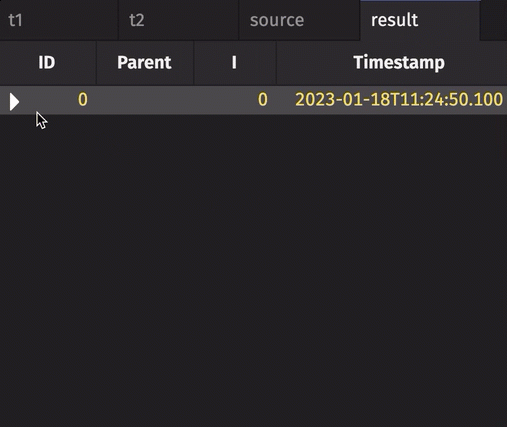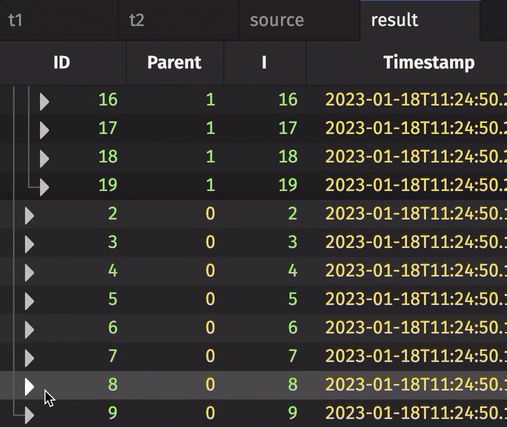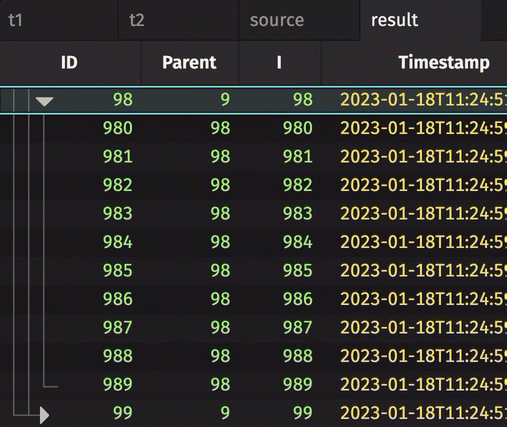
The following example creates a tree table from a real-time table.
from deephaven import empty_table, time_table
from deephaven.constants import NULL_INT
t1 = empty_table(10_000).update_view(
["ID = i", "Parent = i == 0 ? NULL_INT : (int)(i / 10)"]
)
t2 = time_table("PT0.01S").update_view(["I = i % 10_000"]).last_by("I")
source = t1.join(t2, "ID = I")
result = source.tree(id_col="ID", parent_col="Parent")
The following example creates a tree table from a source table that contains orphans. The first omits orphan nodes, while the second promotes them such that they appear in the tree table.
from deephaven.constants import NULL_INT
from deephaven import empty_table
source = empty_table(100).update_view(
["ID = i + 2", "Parent = i == 0 ? NULL_INT : i % 9"]
)
result_no_orphans = source.tree(id_col="ID", parent_col="Parent")
result_w_orphans = source.tree(id_col="ID", parent_col="Parent", promote_orphans=True)