snapshot_when
The snapshot_when method produces an in-memory copy of a source table that adds a new snapshot when another table, the trigger table, changes.
Note
The trigger table is often a time table, a special type of table that adds new rows at a regular, user-defined interval.
Caution
When snapshot_when stores table history, it stores a copy of the source table for every trigger event. This means large source tables or rapidly changing trigger tables can result in large memory usage.
Syntax
Parameters
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| trigger_table | Union[Table, PartitionedTableProxy] | The table that triggers the snapshot. This should be a ticking table, as changes in this table trigger the snapshot. |
| stamp_cols optional | list[str] | One or more column names to act as stamp columns. Each stamp column will be included in the final result, and will contain the value of the stamp column from the trigger table at the time of the snapshot. If only one column, a string or list can be used. If more than one column, a list must be used. The default value is |
| initial optional | bool | Determines whether an initial snapshot is taken upon construction. The default value is |
| incremental optional | bool | Determines whether the resulting table should be incremental. The default value is |
| history optional | bool | Determines whether the resulting table should keep history. The default value is |
Caution
The stamp column(s) from the trigger table appears in the result table. If the source table has a column with the same name as the stamp column, an error will be raised. To avoid this problem, rename the stamp column in the trigger table using rename_columns.
Returns
A new table that captures a snapshot of the source table whenever the trigger table updates.
Examples
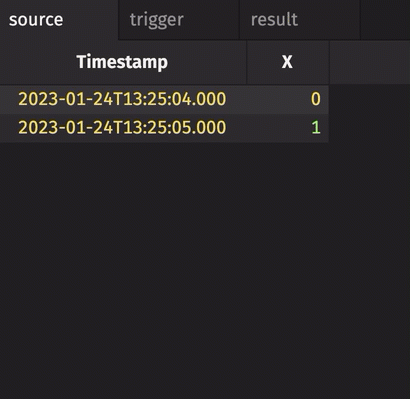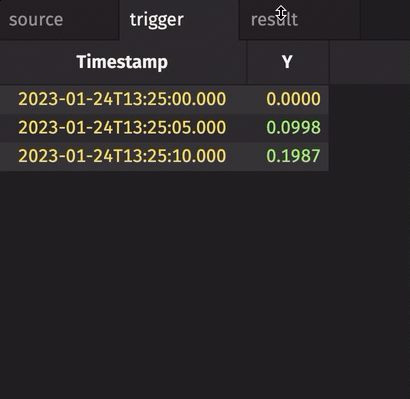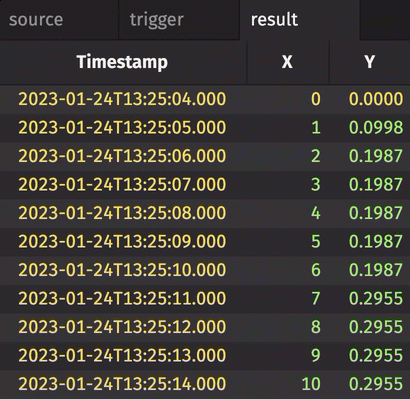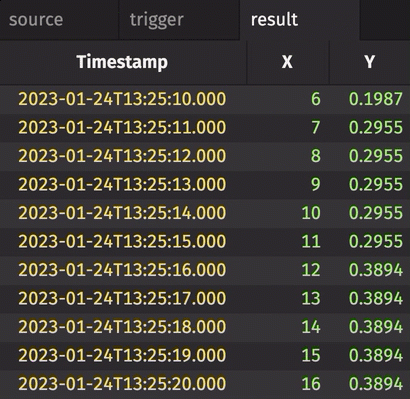
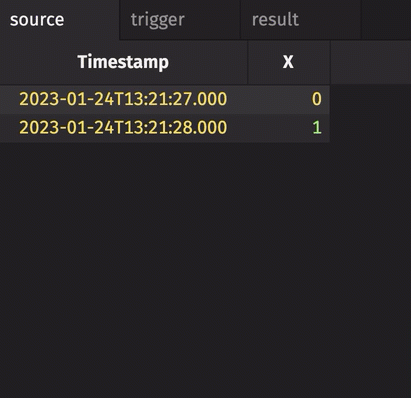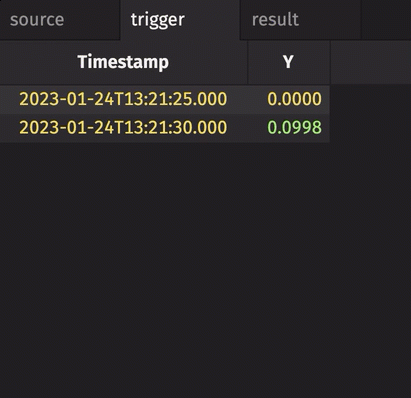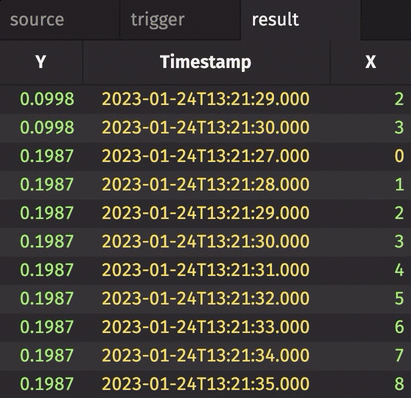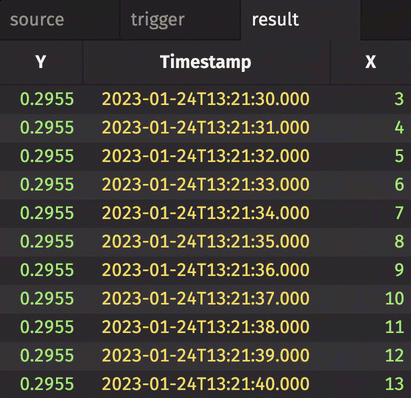
In the following example, the source table updates once every second. The trigger table updates once every five seconds. Thus, the result table updates once every five seconds. The Timestamp column in the trigger is renamed to avoid a name conflict error.
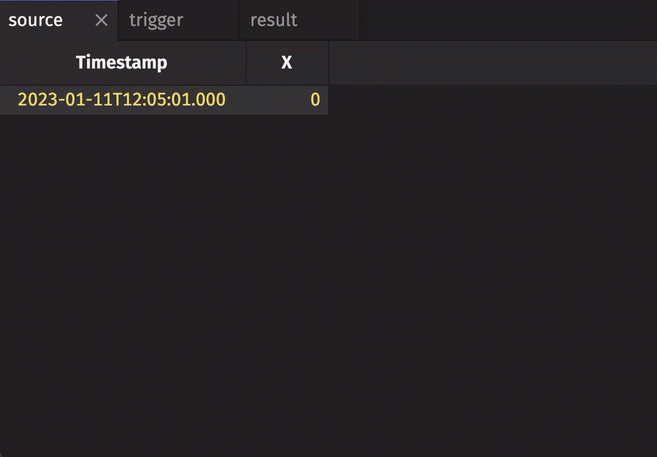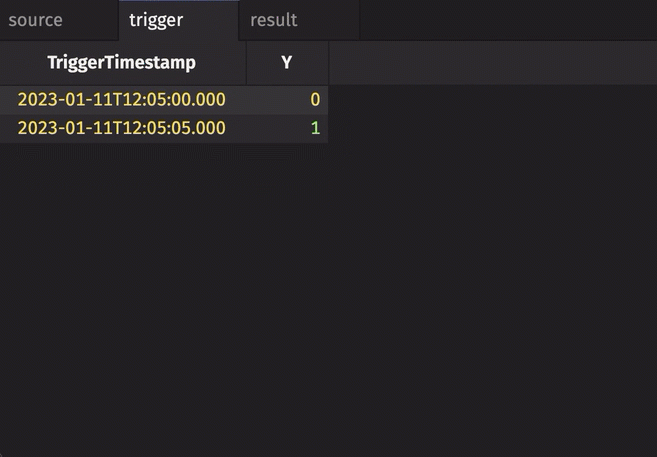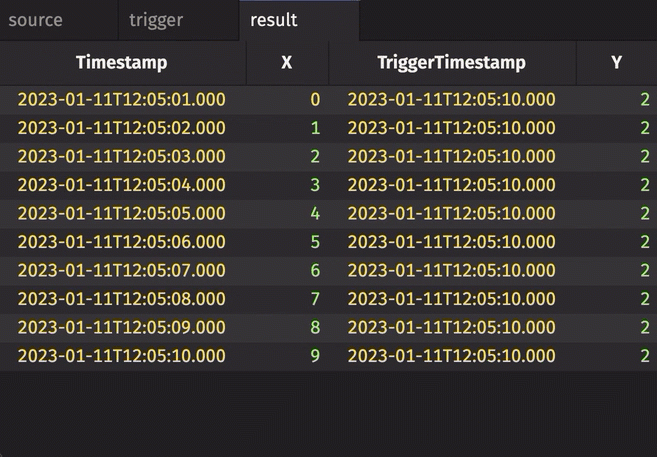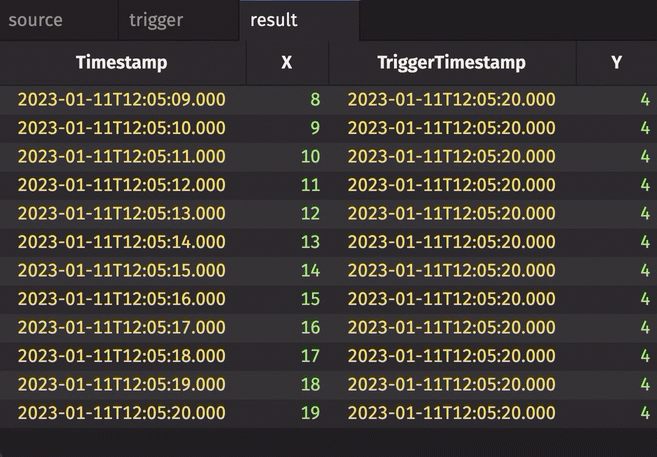
Notice three things:
stamp_colsis left blank, so every column fromtriggeris included inresult.incrementalisfalse, so the entireTriggerTimestampcolumn inresultis updated every cycle and always contains the latest value from theTriggerTimestampcolumn intrigger.historicalisfalse, so only updated rows fromsourceget appended toresulton each snapshot.
In the following example, the code is nearly identical to the one above it. However, in this case, the Y column is given as the stamp key. Thus, the Timestamp column in the trigger table is omitted from the result table, which avoids a name conflict error. This is an alternative to renaming the column in the trigger table.
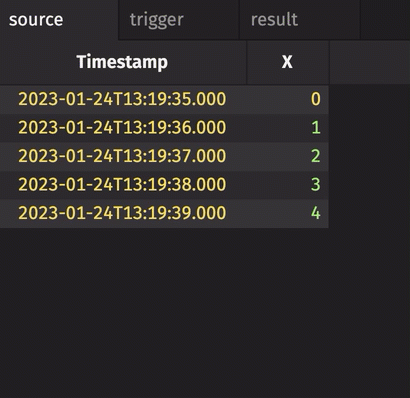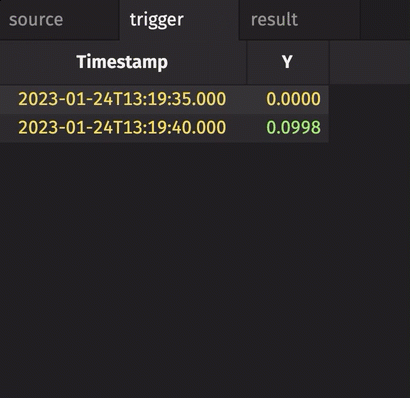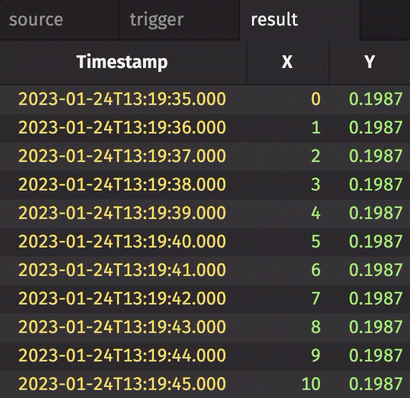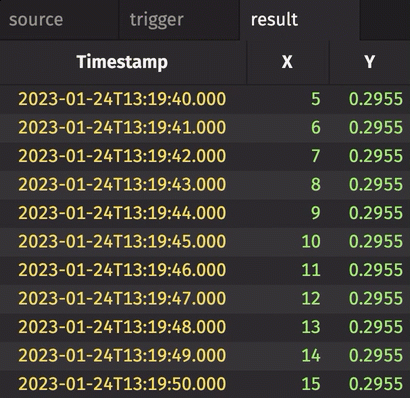
In the following example, history is set to True. Therefore, every row in source gets snapshotted and appended to result when trigger changes, regardless of whether source has changed or not.
In the following example, incremental is set to True. Thus, the Y column in result only updates when corresponding rows in trigger have changed. Contrast this with the first and second examples given above.